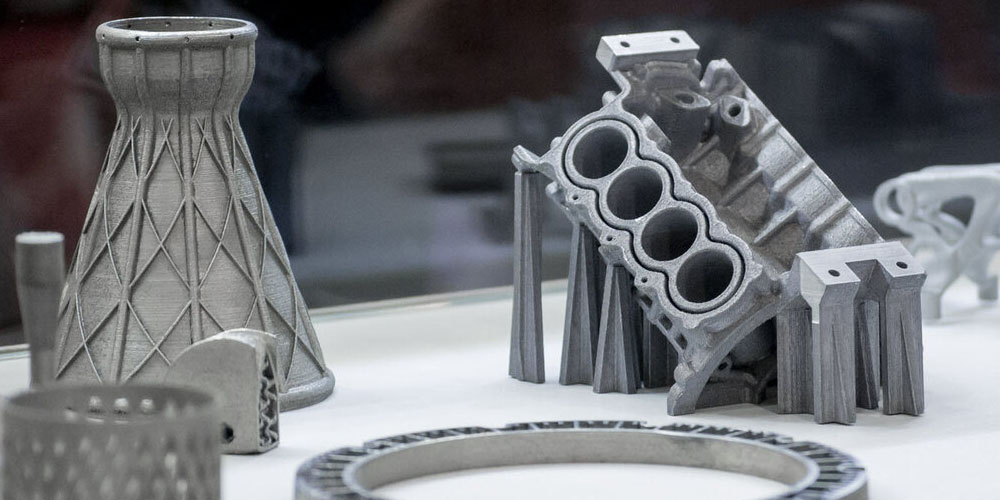
3D prototyping or rapid prototyping is a process of product manufacturing that involves the fast manufacturing of a physical prototype. The prototype is altered in every step to make it better until one that production worthy is developed. Rapid prototyping is time and cost-effective, thanks to the introduction of digital technologies. Different materials with varying properties are used based on several factors, such as what a client wants. In this article, we discuss the rapid prototyping technologies available for use in various applications.
Rapid Prototyping Techniques
There are several 3D prototyping techniques available, but we will expound on the three main ones below.
1. 3D Printing
It is an additive manufacturing process whereby materials are added in layers until the desired shape or form is achieved. The most common application for this technique is rapid prototyping which provides flexibility in terms of materials and speed used to create the prototypes. 3D is known for producing objects at a low cost; however, it’s not ideal for the mass production of items. 3D printing is divided into three depending on the accuracy level, i.e., fused deposition modeling (FDM), Stereolithography(SLA), and Selective laser sintering (SLS).
FDM printing process is the most common and is ideal for use at home or first-run prototypes. Stereolithography is suitable for prototypes with a higher resolution, and SLS is suitable for industrial prototypes since its more specialized than the rest. Examples of applications that use 3D printing include engineering, jewelry design, and architecture.
2. CNC Milling
It is a subtractive technology used in rapid prototyping to develop objects. It involves a cutting tool that cuts on different materials ranging from glass, metal, plastics, and wood. It is a versatile process since it allows all types of cuts on materials, and 3D models can be created from the software and later exported into a format compatible with CNC.
The materials are then placed on the work table, and the mill works on it with reference to the 3D digital model. CNC milling uses cutting tools to make parts into a single item or develops a prototype with several parts and serve the same purpose. This prototyping process is suitable for industries and applications such as medicine, aerospace, aviation, and automotive.
3. Laser Cutting and Engraving
The process applies subtractive manufacturing to produce objects. A laser beam helps to cut precise parts with varying thicknesses with high speed. The parts are usually made from different materials like wood, acrylic, and metal sheets which are later added to details using laser engraving to make the prototype complete. The process can also accommodate hard materials like aluminum, carbon steel, and stainless steel, and some manufacturing industries offer this service to clients. The possibility of using different materials makes laser cutting suitable for use in industries like aerospace, automotive, and the military.
Final Words
Rapid prototyping involves many techniques applicable in multiple industries. Any concept design can be developed into a physical prototype using the correct process and materials.